Driven to Succeed: Exploring the Software Development Methods
To excel in software development, numerous factors should be considered. One of the most critical is selecting the right development methodology. This choice ensures timely delivery and meeting quality standards, yet it depends on variables such as project idea, complexity of architecture, and team dynamics. Understanding these factors deeply is essential for making informed decisions. Let’s explore the most popular practices to help you choose the optimal development methods.
What are the common methods of software development?
Among the variety of popular methodologies, the following are worth considering:
- Behavior Driven Development (BDD)
- Test Driven Development (TDD)
- Data Driven Development (DDD)
- Domain Driven Design (another DDD)
- Feature Driven Development (FDD)
- Event Driven Development (EDD)
- User Driven Development (UDD)
These software development methods pave the way for successful project outcomes. Some are complementary, enhancing each other’s effectiveness, while others demand a meticulous architectural approach. Further throughout the article we dive deeper into their application.
Test Driven Development
Test Driven Development (TDD) is a software design method where tests are created before writing actual code, ensuring thorough testing of each feature. This approach is particularly effective in Agile frameworks with evolving requirements. By prioritizing early testing, TDD often leads to improved software architecture, with responsibilities well-distributed among components and complex procedures simplified into manageable tasks. By continually verifying critical functionalities through automated tests integrated in continuous integration (CI) pipelines, TDD enhances application stability.
Some notable development frameworks that support TDD include: JUnit for Java, Jest for JavaScript testing, PyTest for Python, and NUnit for .NET languages.
Pros:
- Improved code quality: Creating tests encourages developers to assess programmed algorithms and the holistic architecture carefully.
- Refactoring support: With extensive test coverage, developers can modify code confidently, assured that existing functionality remains intact.
- Documentation: Tests serve as documentation, demonstrating how the application should function.
- Simplified debugging: Tests streamline debugging process, offering atomic and straightforward insights into code issues.
- Controlled technical debt: Test-driven approach enhances metrics like maintainability, testability, and changeability.
Cons:
- Initial investment: Introducing tests may initially consume additional time, potentially delaying the feature development.
- Overhead: Managing a substantial test suite can be cumbersome, particularly with frequent changes in requirements.
Behavior Driven Development
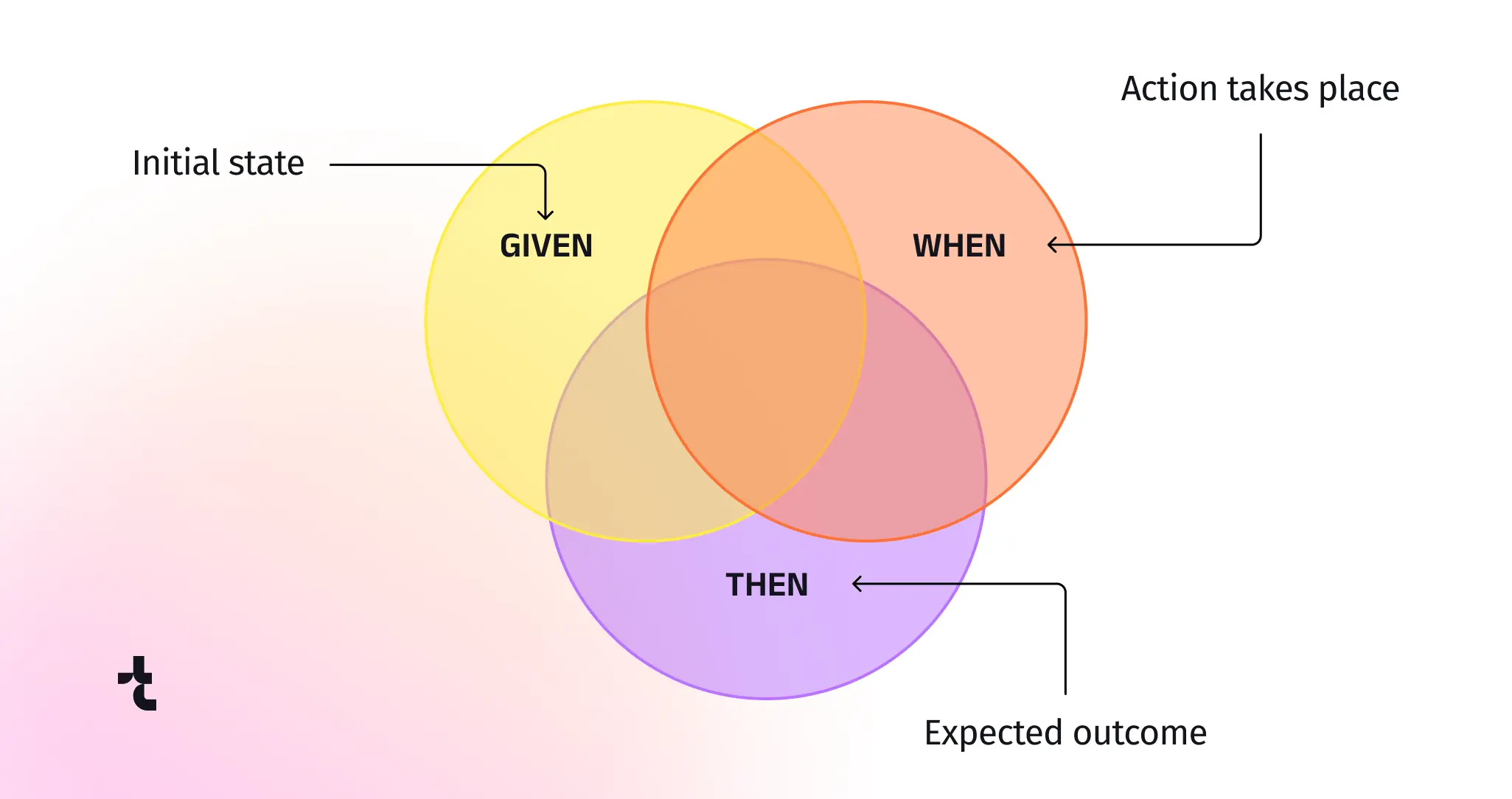
Behavior Driven Development (BDD) is an alternative development method that extends Test Driven Development (TDD) by prioritizing teamwork among technical members and business stakeholders, ensuring everyone is on the same page. In BDD, test scenarios are crafted in natural language using the Given-When-Then structure:
- Given some initial context,
- When an action is performed,
- Then a particular outcome should occur.
Numerous tools enable writing tests in plain language. For instance, SpecFlow for .NET, Behave for Python, and JBehave for Java, while Cucumber offers support for various technologies, including Ruby, Java, and JavaScript.
Pros:
- Improved communication: BDD fosters bridges the gap between software developers and stakeholders who lack a technical background.
- User-centric: Focusing on user behavior ensures that the software closely aligns with user needs and preferences.
- Enhanced documentation: The natural language scenarios serve as both quality benchmarks and reference material, clearly outlining the product’s functionality.
Cons:
- Initial learning curve: Teams new to BDD might require time to learn and adapt to writing behavior specifications.
- Overhead: Writing and maintaining detailed scenarios can be time-consuming, which may slow down development.
Comparing BDD and TDD
BDD is akin to TDD in many ways but takes a unique angle. While TDD utilizes unit tests for development, BDD uses natural language scenarios to test behavior from a user’s perspective. Both methods prioritize writing tests initially, but BDD involves a broader range of stakeholders. In essence, BDD aligns with Agile development best practices by ensuring that the software meets user needs, even as requirements frequently evolve.
Data Driven Development
Data Driven Development (DDD) is a software development method that leverages data to drive every aspect of application creation, from design to development and decision-making. It is particularly valuable in projects that rely heavily on data, like analytics platforms and machine learning systems.
Several tools and technologies support Data Driven Development:
- Data processing frameworks: Apache Hadoop and Apache Spark enable large-scale data processing and analysis.
- Business Intelligence (BI) tools: Tableau and Power BI facilitate data visualization and analysis to guide development decisions.
- Data pipelines: Apache NiFi and Airflow manage data flows between systems efficiently.
Programming languages: Python and R offer extensive libraries and community support for implementing data analysis algorithms.
Pros:
- Decision-making assistance: Insights derived from analyzing collected analytical data can guide more accurate choices for software design.
- Enhanced user experience: By analyzing user behavior and enabling predictive modeling, developers can tailor the application to better meet user needs.
- Optimized performance: Continuous monitoring and analysis of performance metrics help pinpoint bottlenecks and refine the system.
Cons:
- Complexity: Managing big data and ensuring its quality can be intricate and require substantial resources.
- Ensuring privacy: Sensitive data requires strict adherence to regulatory requirements and the implementation of rigorous security measures.
When to use Data Driven Development
Data Driven Development is ideal for projects where data is integral to functionality and user experience. Examples include:
- E-commerce platforms: Personalizing recommendations based on user data.
- Healthcare applications: Analyzing patient data to improve diagnostics and treatment plans.
- Financial services: Risk assessment and fraud detection through data analysis.
- Marketing campaigns: Tailoring strategies and solutions based on consumer data and trends.
Domain Driven Design
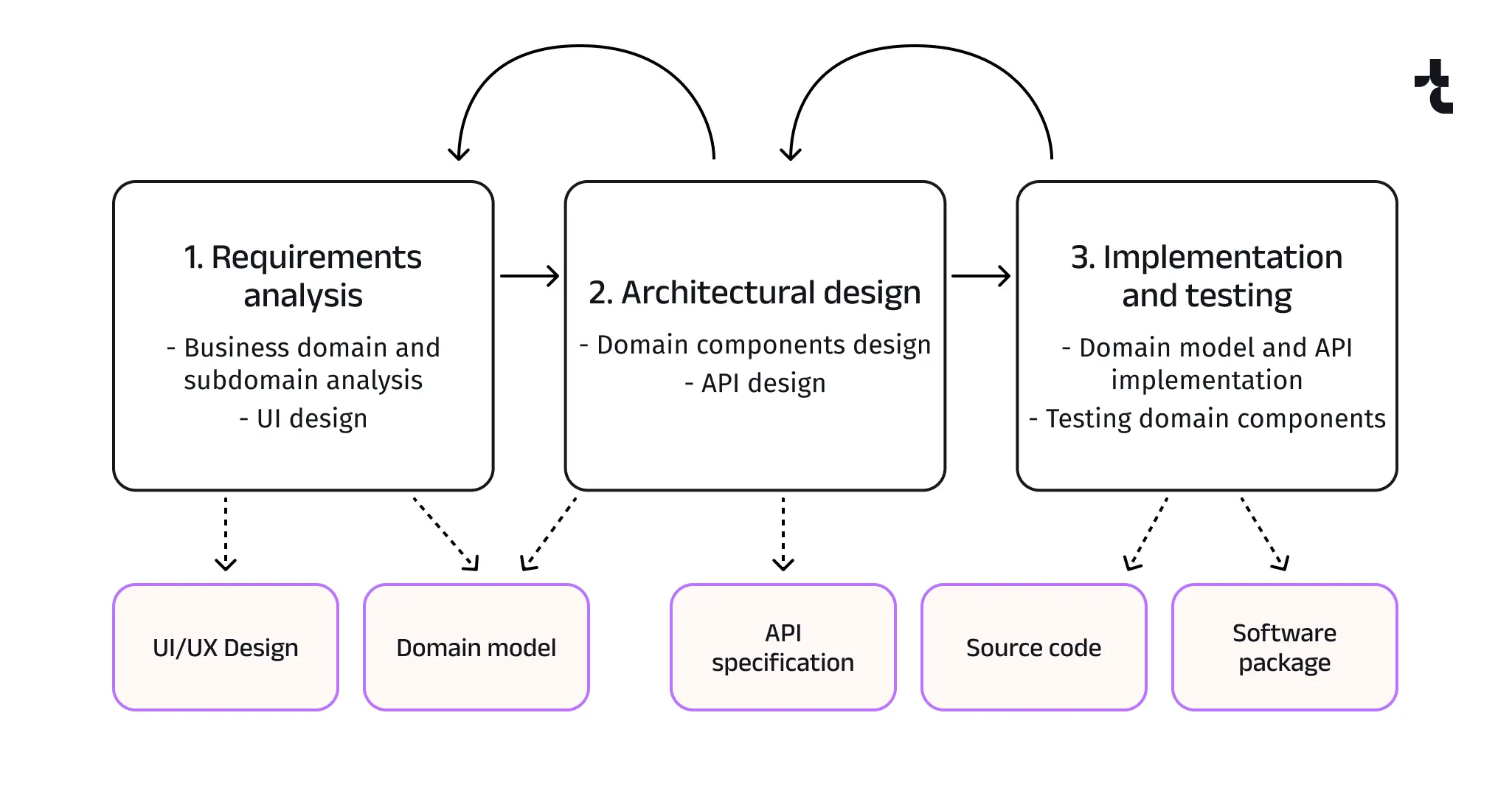
The acronym DDD also stands for Domain Driven Design. However, this methodology differs from Data Driven Development. Domain Driven Design focuses on modeling software to align with complex business domain requirements and stresses collaboration between industry analysts and programmers to ensure a shared understanding of business processes and rules. It’s particularly beneficial for large, complex projects that require deep domain expertise, such as enterprise applications and financial systems.
Tools like UML (Unified Modeling Language) and Miro are invaluable for facilitating Domain Driven Design. Both promote cooperation between subject matter experts and software engineering teams.
Pros:
- Alignment with business goals: Guarantees the software precisely meets business needs.
- Enhanced collaboration: Fosters effective communication between software creators and industry specialists, leading to a deeper understanding of the business domain.
- Maintainability: A well-structured domain model leads to more accurate architecture, which in turn enhances the software’s maintainability and adaptability to changes.
- Scalability: Domain Driven Design’s focus on bounded contexts helps in scaling the application by dividing it into manageable pieces.
Cons:
- Complexity: Implementing such an approach requires a profound grasp of the domain.
- Initial investment: High upfront investment in time and resources to build the domain model and foster effective teamwork.
Comparison with Data Driven Development
Data Driven Development uses data to guide decisions and optimize functionality, while Domain Driven Design models software based on proven knowledge of industry processes to be automated. The latter is an especially powerful development method for building complex and business-critical applications.
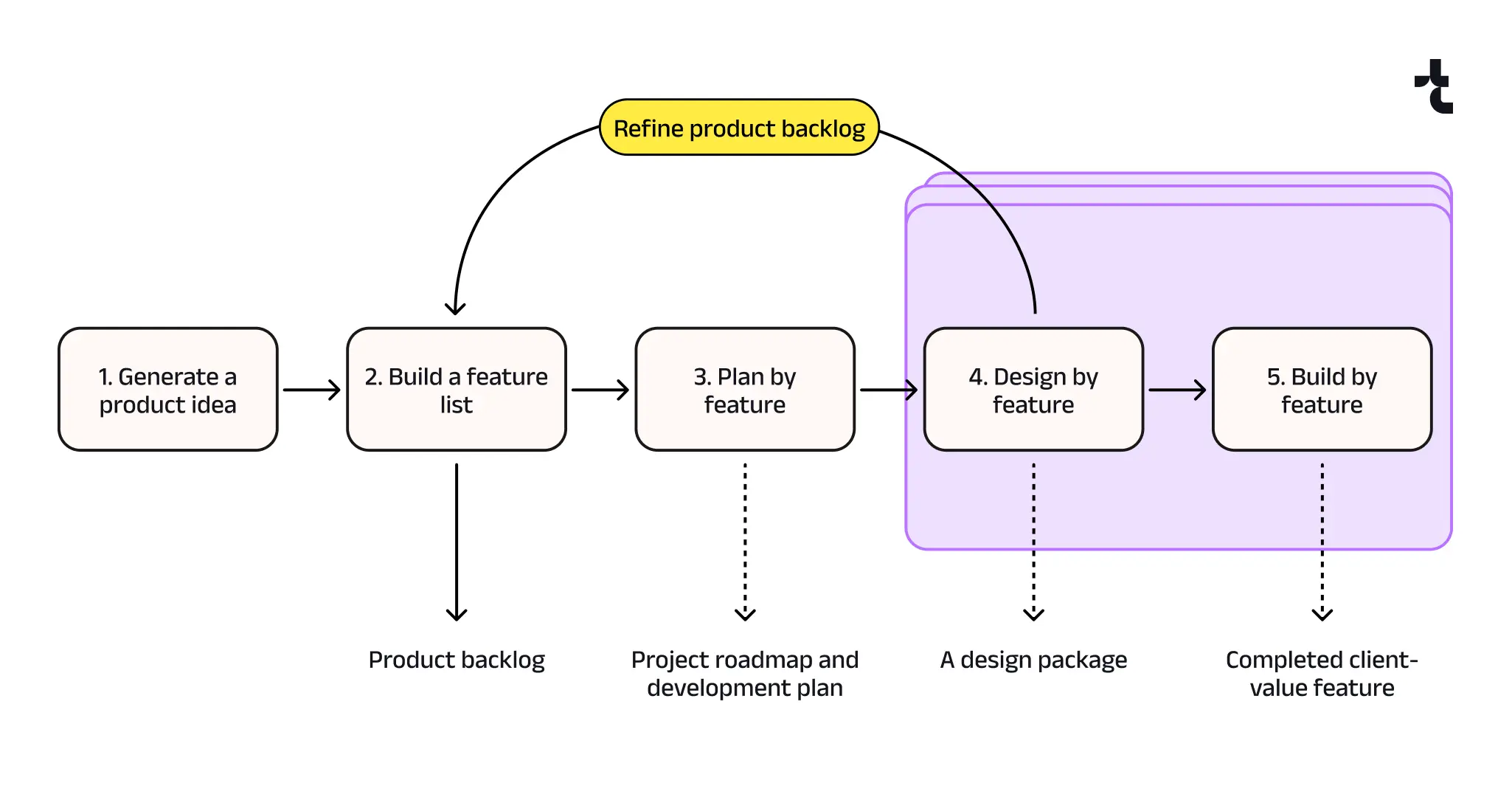
Feature Driven Development
Feature Driven Development (FDD) is an iterative methodology that delivers tangible, working software in short cycles. It focuses on building small, client-valued features that can be delivered in two weeks or less. FDD works well with software development models like Scrum or Kanban.
To implement FDD methodology effectively, it’s advisable to adopt project management tools that support Agile boards and CI/CD, such as Jira, Trello, GitLab, and YouTrack.
Pros:
- Customer-focused: Ensures that development is driven by user-prioritized features, leading to higher satisfaction.
- Predictable processes: Provides a structured, repeatable process, making it easier to manage large projects, such as development of enterprise systems.
- Incremental progress: Delivers working software in short cycles, allowing for regular customer feedback and adjustments.
- Scalability: Scales well for large teams due to its clear structure and focus on individual tasks.
Cons:
- Complexity in feature scope definition: Since projects typically consist of interrelated features, it can be challenging to determine their implementation sequence and isolate a specific feature as a complete functionality for a given iteration.
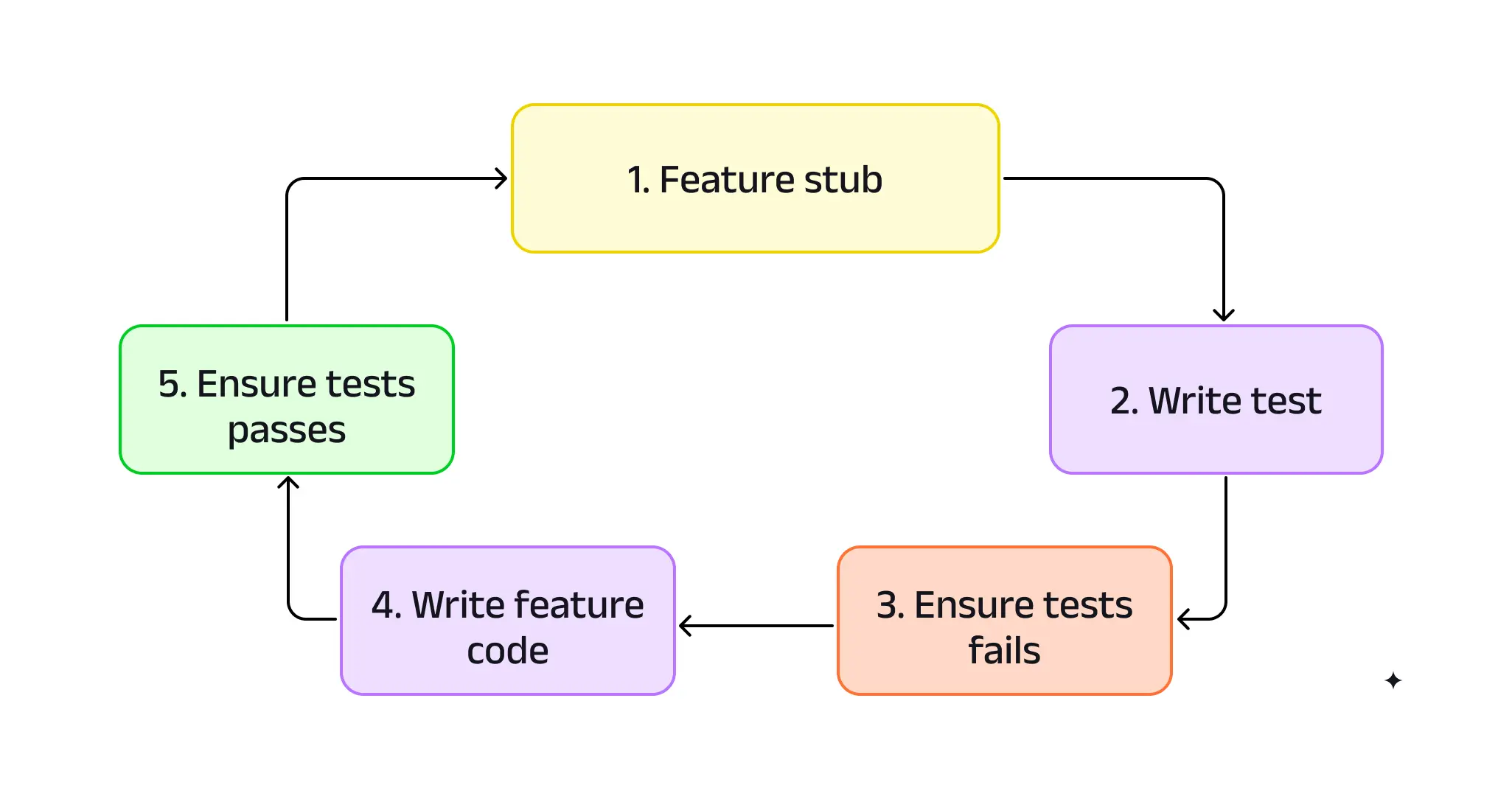
- Overhead: Large features need to be broken down into smaller pieces, accompanied by stub development to fit each iteration. This initially increases implementation overhead, followed by the eventual removal of the stubs.
FDD differs from other software development processes and methodologies by focusing on client-valued features rather than data-driven decision-making or domain knowledge modeling. This makes it ideal for custom software projects that require incremental delivery of ready-to-use functionality.
Event Driven Development
Event Driven Development (EDD) stands out among methods of development with its reactive, event-based approach. It involves designing system components to react asynchronously to messages, fostering a responsive and scalable architecture. EDD is particularly beneficial for applications requiring real-time processing, such as financial trading platforms, live monitoring solutions, online gaming, and social media, where immediate reactions to user actions or system events are essential.
To implement EDD, various tools and development frameworks can be used:
- Message brokers: RabbitMQ, Apache Kafka, and AWS SNS/SQS facilitate message queuing and pub/sub messaging patterns.
- Stream processing: Apache Storm and Apache Flink enable real-time stream processing and analysis.
- Event-driven frameworks: Spring Framework with Spring Cloud Stream, Node.js with Socket.IO, and Akka for building reactive systems.
- Integration platforms: MuleSoft and Apache Camel for integrating various systems through event-driven architectures.
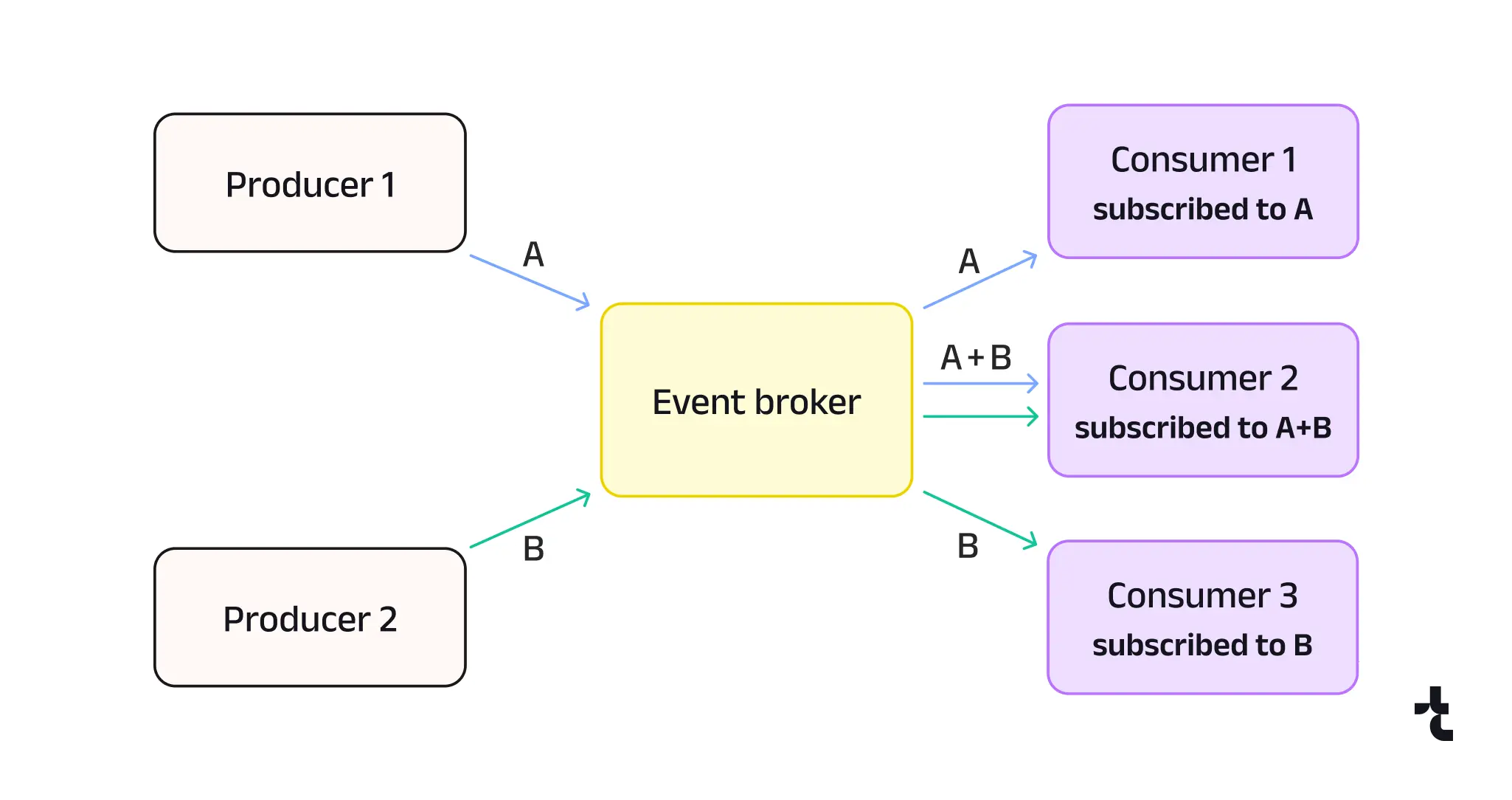
The main idea of Event Driven Development is that the system is designed as a set of loosely coupled components. From the event model perspective, these components may be unaware of each other; some produce necessary data and trigger events, while others subscribe to these events and use the data for their needs.
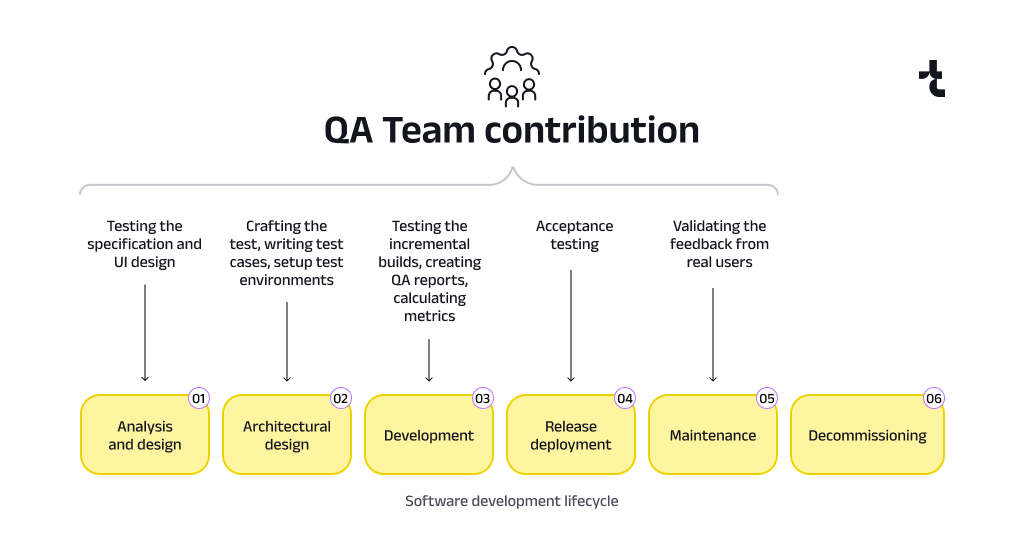
The software development process initiates with a business analyst defining event and data models during the requirement analysis step. Next, an architect designs the high-level architecture, focusing on how the components will interact. DevOps then deploys the necessary technology, including an event broker like Apache Kafka. Only after these steps do software developers start coding. Meanwhile, QA engineers prepare test data and write test scenarios, which are more complex due to the asynchronous nature of the event-driven model.
Pros:
- Scalability: EDD’s asynchronous nature allows for scalable systems that can handle high volumes of events without performance degradation.
- Maintainability and extensibility: Components are loosely coupled, enhancing modularity and making the software easier to maintain and extend.
- Responsiveness: Real-time event processing ensures that applications can respond to user actions and system changes instantly.
- Flexibility: Facilitates complex workflows and integrations by enabling systems to react to various events dynamically.
Cons:
- Complexity: Designing and managing event-driven architectures requires highly skilled software architects.
- Testing challenges: Testing such software can be complex because of its asynchronous nature and the need to simulate event flows.
- Debugging difficulty: Tracing and debugging issues in event-driven systems often require specialized tools and techniques.
Data Driven Development often complements EDD, as optimizing and minimizing transmitted data, along with ensuring conflict-free processing, is crucial in creating an effective event-driven model.
User Driven Development
User Driven Development (UDD) is a software design method that involves engaging end-users throughout the development process, focusing on continuous feedback, iterative design, and direct user testing. Lead users, who are the most active end-users, help by generating and validating ideas and requirements. Non-lead users, meanwhile, test the software and provide feedback. This feedback is then reviewed and, with approval from the lead users, may be incorporated into the project. This approach is particularly valuable in Agile development environments where rapid adjustments to user input are crucial, and it is well-suited for consumer applications, mobile apps, and user-centric web services.
In addition to ticket tracking systems like Jira Service Desk, specific tools such as Figma for interactive UI prototyping, and tools like UserTesting, SurveyMonkey, and Typeform for conducting surveys, can facilitate the collection of user feedback at any stage of development.
Pros:
- User-centric: Ensuring that the final product satisfies users by monitoring user experience.
- Rapid iteration: Encouraging frequent updates and refinements based on user input, leading to a more polished and functional product.
- Reduced risk: By involving users early and often, UDD minimizes the risk of developing unnecessary or poorly designed features.
- Increased engagement: Involving users in the development process can increase their engagement and loyalty to the product.
Cons:
- Resource intensive: Continuously involving users and incorporating their feedback can be time-consuming.
- Potential for scope creep: Constantly adapting to user suggestions may lead to scope creep, where the project expands beyond its original goals.
- Balancing act: Balancing user input with technical feasibility and business goals can be challenging.
- Dependency on user availability: Relying on user feedback requires consistent and reliable user participation, which can sometimes be hard to secure.
Comparison with other methods
User Driven Development fits well within Agile development best practices, emphasizing iterative progress and responsiveness to change. While it shares similarities with Feature Driven Development (FDD), UDD stands out by actively involving real users throughout the development stages, whereas FDD focuses on rapid releases followed by user feedback collection. Unlike other software design methods such as Test Driven Development (TDD) or Behavior Driven Development (BDD), which prioritize code quality and behavior alignment, UDD places the end-user at the center of the development process. This ensures that the final product is not only well-built but also user-friendly.
So many software development methods, which to choose?
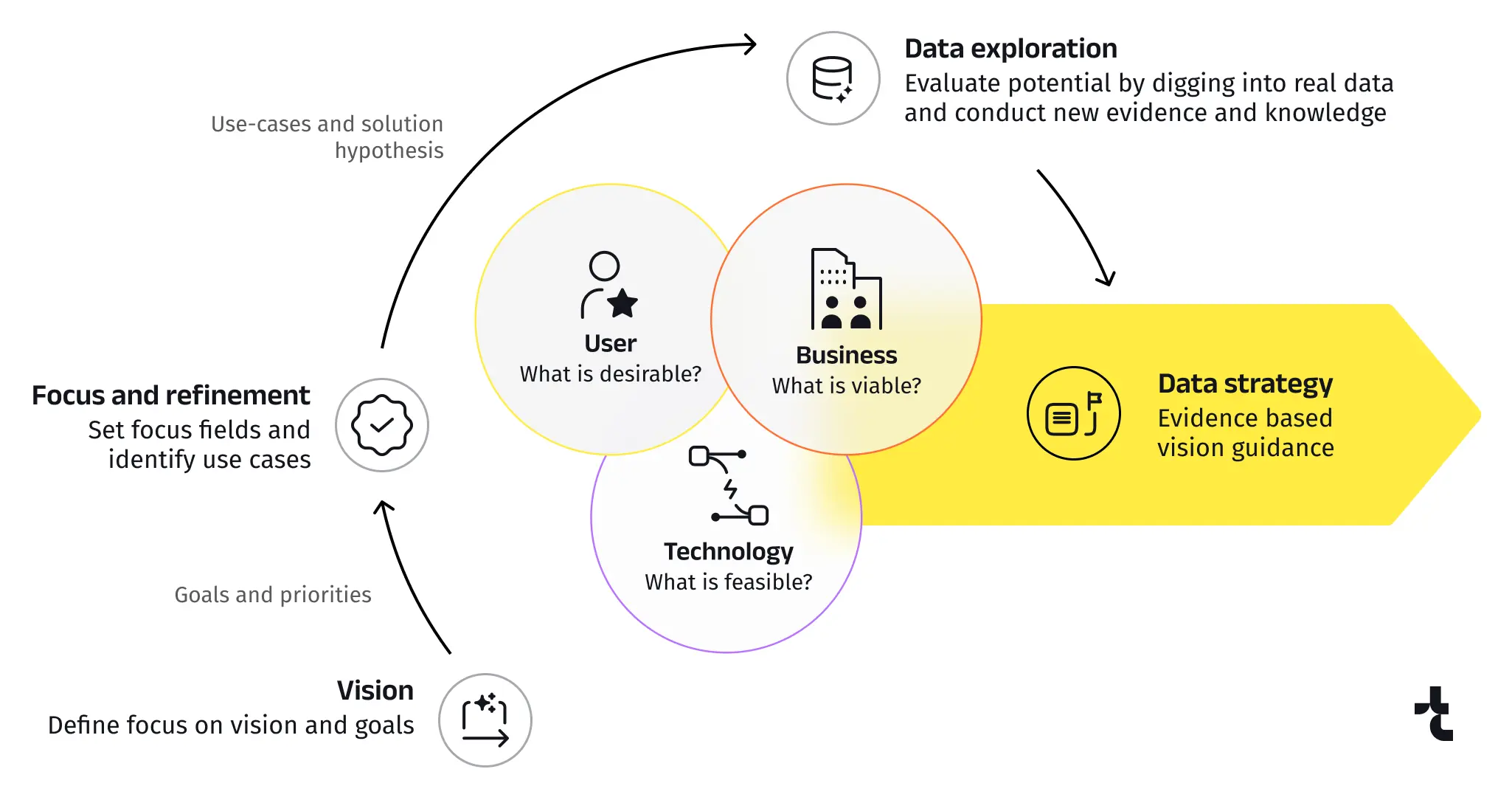
Choosing the right development method depends on many factors and typically occurs during the Elaboration phase. This stage involves refining the project’s vision, identifying risks, and establishing the project’s architecture. Timspark’s technical pre-sales team can design a comprehensive vision for the future software, which will then be used by our architects to select the appropriate methodology. Our skilled DevOps team will ensure the seamless execution of the chosen software development approaches, driving your project to success.
Do you have a project in mind?
References
- About the Unified Modeling Language specification version 2.5.1. The Object Management Group® (OMG®), 2017.
- SQS Queues and SNS Notifications – Now Best Friends. Amazon, 2012.