The Importance of Independent Software Testing Services in Business
September 2, 2025
Developing software is a costly endeavor, and many companies explore cost-cutting by managing functions internally. Testing often seems like the easiest task to handle in-house, but this misconception can lead to significant expenses.
Proper quality assurance (QA) is as critical as professional coding. High-profile cases, such as Toyota’s unintended acceleration issues (2009–2010) due to the software errors or the bug in the Windows 10 October update (2018) causing data loss, highlight the risks of inadequate testing.
To mitigate these risks, companies are increasingly adoptingi ndependent software testing services , also known as third-party QA or outsourced software testing. This approach complements in-house QA by providing an objective perspective, ensuring software meets high standards for reliability, security, and usability.
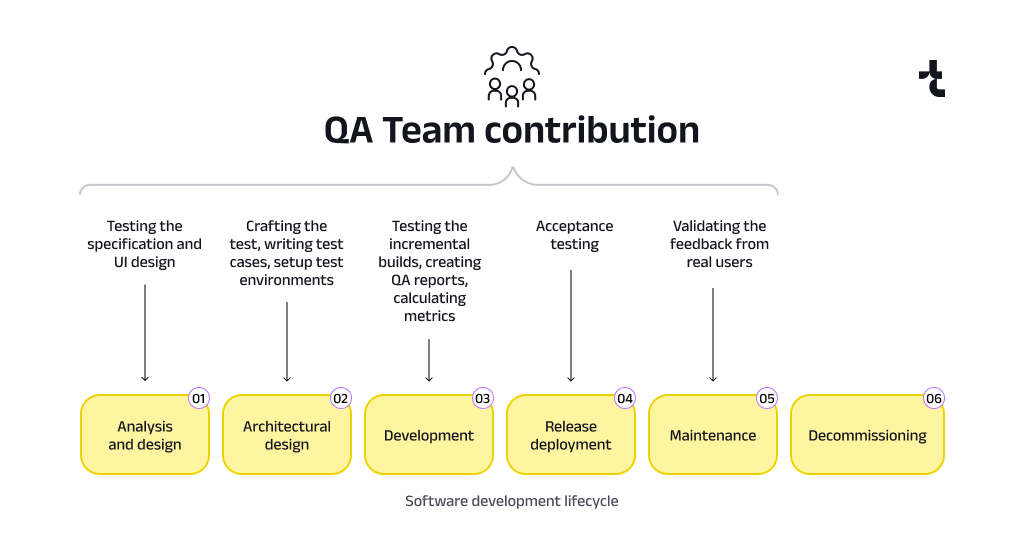
The integral role of QA team
Although it may seem easy, software testing is more than just clicking buttons. The quality assurance process entails multiple steps, with significant emphasis on preparation and documentation: crafting a test plan, developing test cases, scrutinizing software requirements and UI design, generating test data, and configuring necessary environments. Choosing the appropriate tools to track identified issues (such as Atlassian Jira or JetBrains YouTrack) and ensuring the maturity of quality assurance procedures are critical. They eliminate wasting time resources and offer prompt feedback on the build’s suitability for further testing. Robust QA processes mitigate scenarios where rectifying one bug introduces new ones or the implementation of a new feature destabilizes the entire application. And this is just the tip of the iceberg.
Beyond functional testing, QA shoulders the responsibility for software security, performance, and usability. Although it might seem that involving the QA team at the final stage of development for acceptance testing is sufficient, this is a misconception. Quality assurance specialists should be actively involved throughout all stages of software development, starting with validating UI design and requirements. The earlier a problem is detected, the cheaper it is to fix. By the time the software reaches the acceptance testing stage, it should have already been thoroughly examined and be operating according to specifications.
A valid reason behind having a dedicated QA team over programmers verifying their own code is that QA engineers and software developers typically have slightly different goals: programmers aim to make the code functional, while testers strive to uncover defects with negative scenario testing. This collaboration, where programmers create and QA specialists try to break, offers significantly more advantages than relying solely on developers, regardless of their skill level.
What does the customer receive from the QA team’s work? Primarily, a report on the quality of the developed system. Detailed reports show not only the current state of the software being developed but also trends in quality changes, using historical data and various QA metrics (such as the percentage of reopened bugs, the percentage of passed test cases, etc.). Additionally, a proficient QA department offers recommendations on priorities for the next build release. While there may not always be an obvious issue, they can identify indicators that suggest a potential problem under certain conditions.
To ensure high-quality software, particularly when the cost of errors is significant, it is wise to involve an independent testing team. Companies that provide independent software testing services as a service can deliver the best results thanks to certified professionals who adhere to international testing standards such as ISO/IEC/IEEE 29119 and ISO/IEC 25010:2023. Additionally, these independent teams prioritize the software customer’s interests, unlike internal QA specialists who are closely aligned with the development team.
Independent software testing: benefits and risks
Hiring an external QA team is like employing a professional food taster — they provide honest feedback and uncover hidden issues. While in-house teams understand your product’s “recipe,” independent testers bring fresh insights and broad expertise.
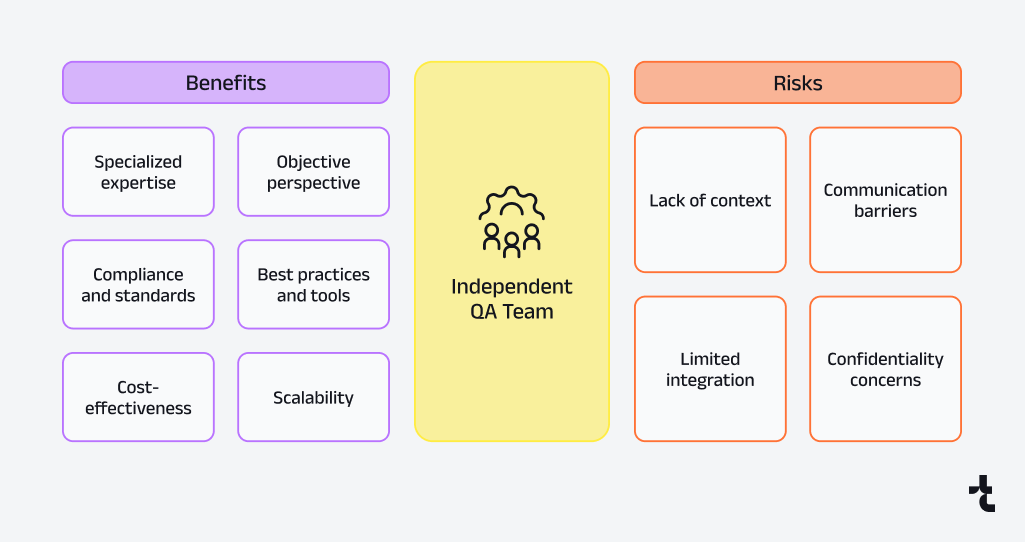
Benefits of Independent QA Services
-
- Objective Perspective: Unbiased feedback free from internal pressures or politics.
- Specialized Expertise: QA engineers with experience across industries and projects.
- Cost Efficiency: Eliminates the need for costly in-house QA infrastructure or full-time staff.
- Scalability: External teams adapt quickly to project demands.
- Compliance with Standards: Certified in standards like ISO/IEC/IEEE 29119 and ISO/IEC 25010:2023.
- Advanced Tools: Access to modern technologies, such as AI plugins for Selenium and SmartBear VisualTest, for thorough testing.
Risks of Outsourcing QA
- Lack of Context: External testers may not fully understand internal processes or culture.
- Communication Barriers: Collaboration between external QA and in-house developers may require extra effort.
- Integration Issues: Challenges aligning with internal tools or workflows.
- Confidentiality Concerns: Sharing sensitive data requires robust security agreements and NDAs.
Mitigation: Clear communication, strong contracts, and secure collaboration tools can minimize these risks, making the benefits outweigh the challenges.
Independent testing as part of quality-centric culture
A compelling product idea can fail without proper implementation. To stay competitive, companies must foster a quality-centric culture, prioritizing reliability and user satisfaction throughout development. Independent software testing supports this by providing objective validation, early defect detection, and continuous improvement.
Elements of a Quality-Driven Approach
- Continuous Improvement: Regularly refining processes and practices.
- Collaboration: Strong teamwork among developers, QA staff, designers, and analysts.
- Customer Focus: Prioritizing end-user needs in all decisions.
- Accountability: Holding teams responsible for quality outcomes.
- Automation: Using modern QA tools to reduce errors and accelerate workflows.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Leveraging QA metrics and analytics for improvements.
Role of DevOps in QA Culture
- Continuous Integration: Timely testing reduces risks.
- Technical Debt Management: DevOps ensures long-term performance and maintainability.
- Integration with Outsourced QA: Well-integrated external QA or DevOps services strengthen quality culture.
All of these aspects can be effectively managed through QA testing as a service. It’s also worth noting that companies specializing in outsourcing testing services increasingly leverage AI tools to bolster task automation and data analysis.
However, creating a quality-driven culture requires more than just hiring seasoned developers and QA specialists. It entails ensuring that all processes work seamlessly together. This is where DevOps comes into play by implementing continuous integration of changes and timely quality checks. Skilled DevOps specialists can help mitigate the inevitable risks associated with outsourcing or other activities, even when the DevOps service itself is third-party. Furthermore, DevOps plays a crucial role in controlling technical debt by ensuring code quality and performance.
Trends in QA testing services
Considering recent advancements in software development—such as AI evolution, virtual and augmented realities, digital assets, virtual payments, and smart devices—the demand for high-quality software is more critical than ever. The cost of errors is growing exponentially, affecting users of all ages, from infants to the elderly.
Key QA Trends:
-
- Shift-Left Testing: Integrating QA early in development to reduce costs and time to market.
- Shift-Right & Chaos Engineering: Testing in production-like environments (e.g., Netflix’s Chaos Monkey).
- Automation Testing: Expanding automated validation to speed up releases.
- Security Testing: Addressing sophisticated AI-driven cyber threats.
- Performance Engineering: Designing systems with performance as a priority from the start.
- AI and Machine Learning in QA: Automating complex test scenarios and predicting defects.
- Ethical & Usability Testing (DEI): Ensuring software is inclusive, accessible, and equitable.
Independent software testing services by Timspark
We cover a whole range of independent software testing services across diverse industries, employing best practices and cutting-edge AI testing tools like various AI plugins for Selenium, SmartBear VisualTest, and more. Our team of highly experienced QA engineers, many of whom are certified by ISTQB and CMSQ, ensures the creation and support of tailored testing processes.
Need professionalQA and testing services?
FAQ: Independent Software Testing
What is independent software testing?
It involves assessing software quality through an external QA provider, complementing or replacing in-house testing.
How is independent testing different from in-house QA?
Independent QA offers objectivity, scalability, and expertise, while in-house QA provides deep product familiarity.
What are the benefits of outsourcing QA?
Cost savings, faster releases, unbiased evaluation, access to advanced tools, and compliance with standards.
What are the costs of independent testing services?
Costs vary by scope, complexity, and duration, but are typically more cost-effective than maintaining an in-house team.
Which industries benefit most from independent QA?
Industries with high error costs, such as fintech, healthcare, automotive, and telecom, gain significant advantages.
References
- Toyota’s acceleration testing still inadequate, House members say. Los Angeles Times, 2010.
- Microsoft Confirms Windows 10 Update Mistake — Was Your Data Lost? Forbes, 2018.
- Chaos Engineering Saved Your Netflix Extreme stress testing of online platforms has become its own science. IEEE Spectrum, 2021.
- ISO/IEC/IEEE 29119-1:2022 Software and systems engineering — Software testing. ISO, 2022.
- ISO/IEC 25010:2023 Systems and software engineering — Systems and software Quality Requirements and Evaluation (SQuaRE) — Product quality model. ISO, 2023.