Anna Rozhentsova, Content Manager
July 4, 2024
Like humans have gone through their evolution path, so now does artificial intelligence, with human assistance. Becoming smarter, quicker, and more adept at tackling complex tasks already seems the natural way of AI evolving. Its progress is rapidly reshaping technology and expanding its applications.
To fully grasp the AI’s potential, challenges and possibilities it may bring to businesses and the technological world, we need to answer the following questions: How has artificial intelligence evolved? How fast is AI evolving? What are the main stages of AI? What stage of AI are we in?
Understanding AI in a nutshell
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is basically the emulation of human intelligence in machines programmed to think and perform tasks like humans. The powerful AI tools we use today stem from computing breakthroughs spanning over 70 years, from code breakers in the Second World War to the very first pattern-recognition networks in the 1950’s. As AI tackles increasingly complex tasks, we face the birth of new AI models, each offering distinct levels of functionality.
Evolution stages of artificial intelligence
Tracing the stages of artificial intelligence is no less exciting than watching the periods of human history. While different approaches highlight its evolution timeline, we opted for a historical perspective on the AI advancements timeline, to uncover pivotal milestones shaping and laying its foundation for today’s thriving AI ecosystem.
The starting point of creating artificial intelligence goes back to the mid-20th century. The pioneering moment in AI was Alan Turing’s 1950 paper “Computing Machinery and Intelligence”, proposing the concept of machines capable of simulating human intelligence.
The official birth of AI as an academic discipline is credited to the 1956 Dartmouth Conference. This gathering brought together researchers to explore and lay the groundwork for AI, marking its emergence as a recognized field of study.
According to the historical approach, researchers break down the AI evolution into several distinct stages.
Birth of artificial intelligence: This era marked the beginning of AI discussions. Early machines capable of playing games like checkers were developed, and Alan Turing introduced his famous test to determine if a machine’s intelligence was equivalent to a human’s.
Early successes: Many AI laboratories were established, and AI received significant financial backing. Research focused on teaching AI natural languages like English. Key achievements include Japan’s first human-like robot, “WABOT,” the introduction of the conversational AI model “ELIZA,” and the creation of the first expert system, “Dendral.”
First AI Winter: Due to slow progress in AI research, partly because of limited computing power, the field experienced a “winter” period that significantly hindered its advancement.
Boom: During this phase, the first expert systems with knowledge in specific fields were designed. AI researchers realized the importance of extensive knowledge bases for AI.
Second AI Winter: Funding for AI research was cut again, largely because AI systems were considered too expensive to maintain.
AI Implementation: AI began to be integrated into various industries. Due to its tarnished reputation from the 20th century, it was often rebranded under different names.
Deep Learning and Big Data: AI interest surged to a “frenzy” level, as described by the New York Times. Significant advancements were made thanks to the development of Deep Learning and Big Data technologies.
AI Era (or Second AI boom): We are currently in this period. Large databases and language models enable the creation of highly proficient AI systems. AI automation is widely used, and generative AI has captivated millions and is now accessible to the general public.
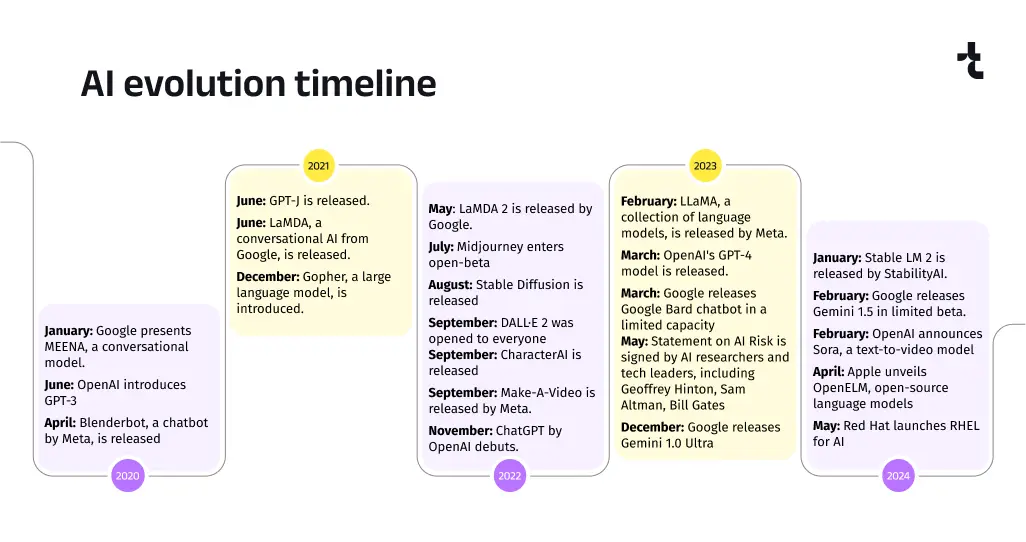
Diving deeper, after analyzing open online sources, we traced the milestones of AI evolution by emergence of popular platforms, text and language models starting from the year 2020. Here are the most significant events that became the cornerstones for the era of AI.
2020
January: Google presents MEENA, a conversational model.
June: OpenAI introduces GPT-3
April: Blenderbot, a chatbot by Meta, is released
2021
June: GPT-J is released.
June: LaMDA, a conversational AI from Google, is released.
December: Gopher, a large language model, is introduced.
2022
May: LaMDA 2 is released by Google.
July: Midjourney enters open-beta
August: Stable Diffusion is released
September: DALL·E 2 was opened to everyone
September: CharacterAI is released
September: Make-A-Video is released by Meta.
November: ChatGPT by OpenAI debuts.
2023
February: LLaMA, a collection of language models, is released by Meta.
March: OpenAI‘s GPT-4 model is released.
March: Google releases Google Bard chatbot in a limited capacity
May: Statement on AI Risk is signed by AI researchers and tech leaders, including Geoffrey Hinton, Sam Altman, Bill Gates
December: Google releases Gemini 1.0 Ultra
2024
January: Stable LM 2 is released by StabilityAI.
February: Google releases Gemini 1.5 in limited beta.
February: OpenAI announces Sora, a text-to-video model
April: Apple unveils OpenELM, open-source language models
May: Red Hat launches RHEL for AI
As we now have a broader picture of AI evolving, we can delve into exploration of AI classifications reflecting how these advancements are reshaping industries and driving innovation.
Decoding the classifications of AI
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming many facets of our lives, from virtual assistants to intricate problem-solving applications. However, AI systems vary greatly in their levels of operation and functions, and therefore, its application in the business and tech sphere. Let’s explore the most vivid of them.
AI classifications by capability
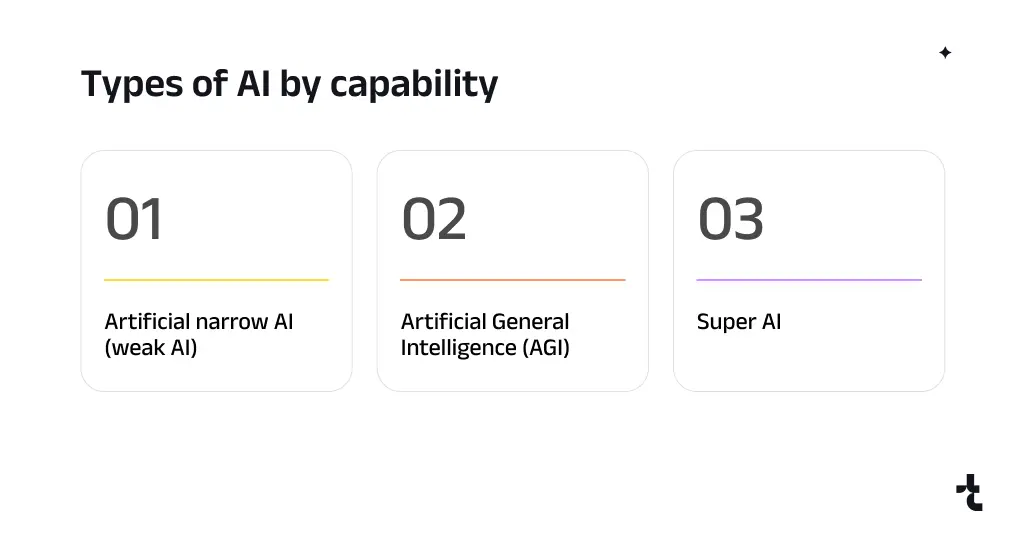
According to capability, AI can be divided into three types: Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI), or weak AI, Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), Artificial Superintelligence (ASI).
1) Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI), or weak AI
Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI), also known as Weak AI, is the only type of AI that exists today. ANI can be trained to execute a specific or limited task, often more efficiently and accurately than a human. Yet, it cannot function beyond its assigned role. It is like a calculator designed to perform complex mathematical operations, but it cannot perform tasks outside of calculations. Instead, it specializes in a single subset of cognitive abilities. Some examples of Narrow AI are Siri, Amazon’s Alexa, and IBM Watson. OpenAI by ChatGPT is also considered a form of Narrow AI because it is limited to the task of text-based interaction.
2) Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)
Artificial General Intelligence, also known as Strong AI, is currently only a theoretical concept. In the ideal world, AGI would be able to use past knowledge and skills to accomplish new tasks in different contexts without requiring human intervention for training. This adaptability and wide-ranging skill set would distinguish AGI from the more specialized AI we see today.
3) Artificial Superintelligence (ASI)
Artificial Superintelligence (ASI), or Super AI, is likewise only theoretical. If brought to reality, ASI is supposed to exceed human intelligence, capable of thinking, reasoning, learning, and making decisions. Moreover, to experience emotions, have needs, and hold beliefs and desires of their own. Luckily, we still have some time before the real rise of Super AI.
AI classifications by functionality
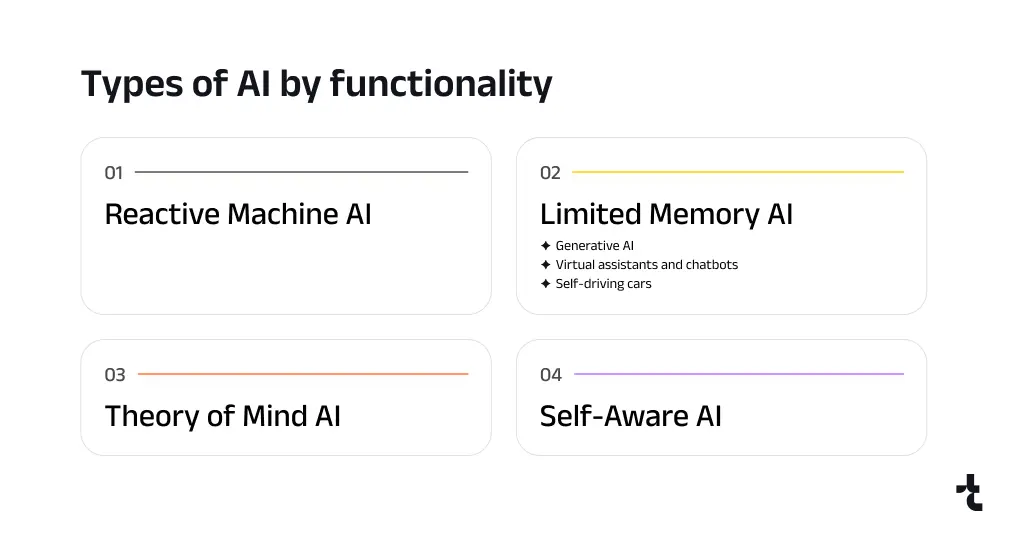
According to functionality, AI can be divided into: Reactive Machine AI, Limited Memory AI, Theory of Mind AI, and Self-Aware AI.
1) Reactive Machine AI. It consists of systems without memory, designed for executing specific tasks and operate only with currently available data. Reactive Machine AI originates from statistical mathematics and can analyze extensive amounts of data to generate seemingly intelligent outputs. Examples include IBM’s Deep Blue and the Netflix Recommendation Engine.
2) Limited Memory AI. Unlike Reactive Machine AI, this form of AI can recall past events and outcomes and monitor specific objects or situations over time. Limited Memory AI can use past- and present-moment data to decide on a course of action most likely to help achieve a desired outcome. However, while Limited Memory AI can use past data for a specific amount of time, it can’t retain that data in a library of past experiences to use over a long-term period. As it’s trained on more data over time, Limited Memory AI can improve in performance.
In contrast to Reactive Machine AI, Limited Memory AI can remember past events and outcomes and track specific objects or scenarios over time. This type of AI can utilize both historical and current data to determine the most effective course of action to achieve a desired result. Yet, Limited Memory AI cannot store this data in a long-term repository, but can enhance its performance thanks to being trained on more data over time.Here are the most vivid examples of Limited Memory AI.
Generative AI like ChatGPT, Bard and DeepAI rely on limited memory AI capabilities to generate the next word, phrase or visual element within the content they generate.
Virtual assistants and chatbots such as Alexa, Siri, Google Assistant, IBM Watson Assistant, and Cortana utilize natural language processing (NLP) and Limited Memory AI to comprehend questions and requests, take appropriate actions, and formulate responses.
Self-driving cars employ Limited Memory AI to perceive their surroundings in real time and make informed decisions on when to accelerate, brake, or turn.
3) Theory of Mind AI. One of the General AI categories, although not yet created, Theory of Mind AI is predicted to understand the thoughts and emotions of others. Potentially this understanding would enable the AI to form human-like relationships. By inferring human motives and reasoning, Theory of Mind AI could personalize its interactions based on individual emotional needs and intentions. Also, Theory of Mind AI would be able to comprehend and contextualize artwork and essays, a capability that today’s generative AI tools lack.
4) Self-Aware AI. It is a type of functional AI for applications that would have super intelligent capabilities. Similar to Theory of Mind AI, Self-Aware AI remains purely theoretical. If it were realized, it would be able to comprehend its own internal states and characteristics, as well as human thoughts and emotions. Additionally, it would possess its own emotions, needs, and beliefs.
AI classifications by technology
The diverse technologies within AI offer a spectrum of capabilities to meet specific business needs. By integrating these technologies, companies can uncover new avenues for innovation.
Let’s dive into types of AI according to technology.
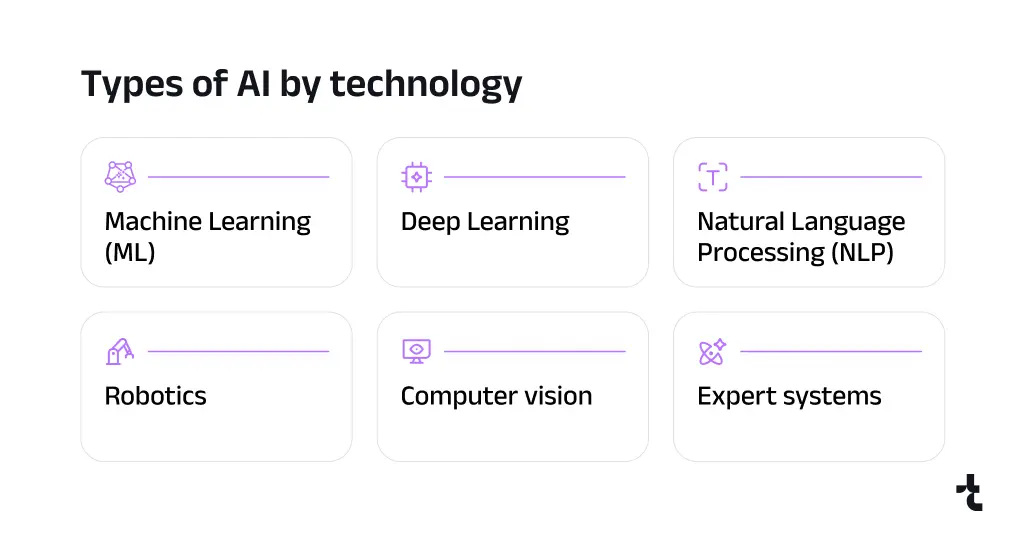
1) Machine Learning (ML)
Machine learning algorithms can analyze large datasets to identify trends and make predictions. For instance, in finance, ML can predict stock market trends or detect fraudulent activities.
Benefits for business: Through predictive analysis and automation ML technology enables businesses to make data-driven decisions, improve efficiency, and enhance customer satisfaction.
2) Deep Learning
A branch of ML, Deep Learning involves neural networks with multiple layers. It is used in image and speech recognition, which can be applied in healthcare for diagnosing and treating diseases from medical images and in customer service for automating voice assistants.
Benefits for business: Deep learning allows for more precise and complex data analysis, fostering innovations in fields like autonomous driving, personalized healthcare, and enhanced security systems.
3) Natural Language Processing (NLP)
NLP allows machines to comprehend and interact with human language. In customer service, chatbots and virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa leverage NLP to manage inquiries. In the legal and finance sectors, NLP can automate the examination of documents and contracts.
Benefits for business: NLP assists businesses in enhancing customer communication, automating repetitive tasks, and extracting valuable insights from unstructured data, like social media and customer reviews.
4) Robotics
Robotics focuses on creating and using robots to perform various tasks. In manufacturing, robots assemble products and handle logistics. In retail, robotic process automation (RPA) manages inventory and helps with order fulfillment.
Benefits for business: Robotics boosts productivity, lowers labor costs, and ensures precision, resulting in more efficient operations and higher-quality products.
5) Computer vision
Computer vision enables machines to understand and make decisions based on visual input. In marketing, it can personalize customer experiences by recommending products based on past behavior, or optimizing advertisement to make it more targeted thus distributing resources wisely. In agriculture, computer vision provides monitoring for crop health and automates harvesting.
Benefits for business: Computer vision unlocks opportunities for quality control, automating visual inspections, and creating unique customer experiences through augmented reality and visual search technologies.
6) Expert systems
Expert systems mimic the decision-making skills of human experts. In healthcare, they aid doctors in diagnosing illnesses. In finance, they assist with investment strategies and risk management.
Benefits for business: Expert systems allow businesses to harness specialized knowledge, enhance decision-making processes, and offer reliable and precise solutions to complex issues.
As AI technology keeps evolving, its applications in the business world will only grow. From optimizing supply chain logistics to transforming customer service with chatbots and virtual assistants, the possibilities are vast. Companies that embrace and implement ready-to-use AI tools or custom AI solutions now will be poised to lead their industries, staying ahead in the marketplace. Timspark is ready to support you on this journey to innovation with custom AI solutions.
Looking for an AI advancement for your business?
References
- Understanding the different types of artificial intelligence. IBM, 2023.
- Types of Artificial Intelligence That You Should Know in 2024. Simplilearn, 2024.
- Generative AI vs. other types of AI. Adobe, 2024.
- The state of AI in early 2024: Gen AI adoption spikes and starts to generate value. McKinsey, 2024
- History of artificial intelligence. Wikipedia, 2024.
- A history of AI. Oxford, 2024.
- Top 10 Most Popular AI Tools That You Need to Use in 2024. Technopedia, 2024.
- Our 10 biggest AI moments so far. Google, 2023.
- AI timelines: What do experts in artificial intelligence expect for the future? Our World in Data, 2023